- Overview
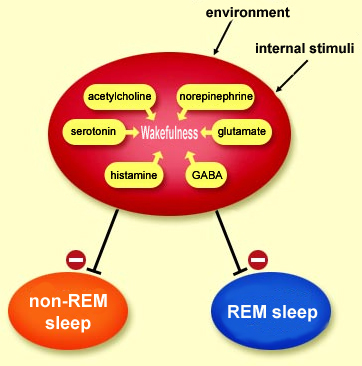
- non-rapid eye movement (NREM)
- rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
- breathing becomes irregular,
- blood pressure rises,
- and there is loss of muscle tone (paralysis). However, the brain is highly active, and the electrical activity recorded in the brain by EEG during REM sleep is similar to that recorded during wakefulness. REM sleep is usually associated with dreaming. REM sleep accounts for 20-25% of the sleep period.
RBD is usually seen in middle-aged to elderly people (more often in men).
- REM Sleep Disorder Causes
RBD often precedes the development of these neurodegenerative diseases by several years. In one study, 38% of patients diagnosed with RBD subsequently developed Parkinson disease within an average time of 12-13 years from the onset of RBD symptoms. The prevalence of RBD is increased in persons with Parkinson disease and in multisystem atrophy where it is observed in 69% of these patients. The relationship between RBD and Parkinson disease is complex; however, not all persons with RBD develop Parkinson disease.
- REM Sleep Disorder Symptoms
The dream-enacting behaviors are usually nondirected and may include punching, kicking, leaping, or jumping from bed while still asleep.
The person may be awakened or may wake spontaneously during the attack and vividly recall the dream that corresponds to the physical activity.
- When to Seek Medical Care
- Exams and Tests
The neurologic examination is often normal. However, symptoms and signs of Parkinson disease, such as hand tremor at rest, slowness in movement, and muscle stiffness (rigidity) that may suggest an underlying neurologic cause of REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD), should be considered.
Polysomnography
Polysomnographic video recording is the single most important diagnostic test in persons with RBD. This test is usually conducted in a sleep study center. The person undergoing testing is required to sleep at the center while the following parameters are monitored:
- Electrical activity of the brain (electroencephalogram [EEG])
- Electrical activity of the heart (electrocardiogram [ECG])
- Movements of the muscles (electromyogram)
- Eye movements (electrooculogram)
- Respiratory movements
Additionally, the video recording shows body movements coinciding with the EEG pattern of REM sleep.
Imaging studies
Imaging studies (for example, CT scan and MRI of the brain) are not routinely indicated in persons who have no neurologic cause of RBD, but they may be done if some abnormality is detected during neurologic examination. Imaging studies should also be considered in younger patients (younger than age 40) where there is no known precipitant cause such as alcohol or medication use (see Causes).
Medications
Clonazepam (Klonopin) is highly effective in the treatment of REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD), relieving symptoms in nearly 90% of patients with little evidence of tolerance or abuse. The response usually begins within the first week, often on the first night. The initial dose is 0.5 mg at bedtime, with some persons requiring a rapid increase to 1 mg. With continued treatment for years, moderate limb twitching with sleep talking and more complex behaviors can reemerge. The treatment should be continued indefinitely, as violent behaviors and nightmares promptly recur with discontinuation of medications in almost all persons with RBD.Other medications, such as tricyclic antidepressants, may be effective in some persons with RBD. However, tricyclics are also known to precipitate RBD in some patients.
Source:
- REM Sleep Behavior Disorder http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1188651-overview
For More Information
American/National Academy of Sleep MedicineNational Sleep Foundation
National Center on Sleep Disorders Research
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute


No comments:
Post a Comment